OS Scenario Extension Development Documentation
chaosblade-exec-os is a basic resource scenario project, such as CPU, memory, process, network, disk and other system resource basic scenarios. This article introduces the basic resource scenario extension in detail from four aspects: project engineering, execution process, scenario extension, and packaging test.
Project Structure
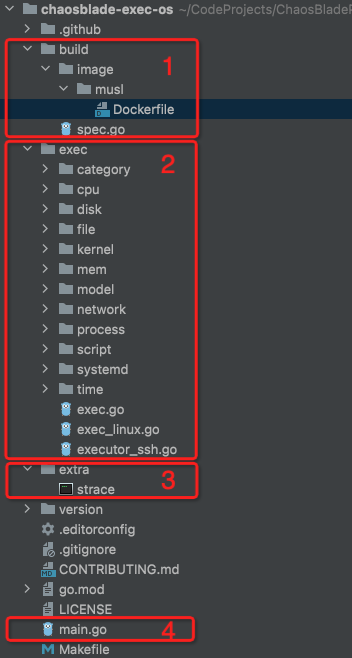
The code of this project consists of four parts:
build is a cross-platform packaging directory.
exec is the implementation code of each scenario.
extra is a dependent third-party tool.
main.go is the scene execution entry.
Execution Flow
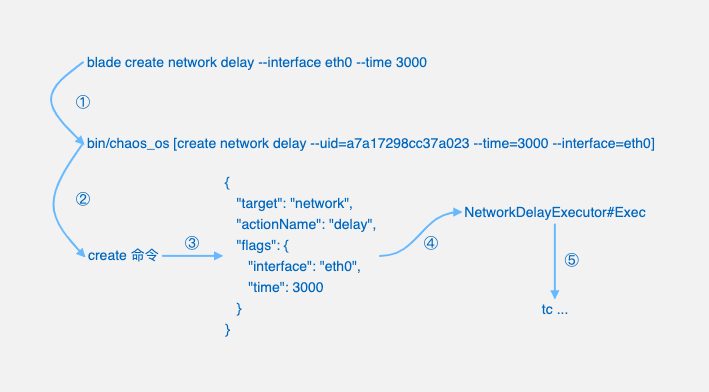
Executing the basic resource scene through blade will call
bin/chaos_osfile to run.bin/chaos_oswill parse the command parameters to identify whether to create an experiment or destroy an experiment.Convert experiment parameters to experiment model object.
Call the corresponding experiment executor to execute.
Scenario Extension
This article takes three new scenarios of Linux system shutdown, power off, and reboot as examples to introduce in detail how to expand the system scenarios in the chaosblade-exec-os project.
Scenario Realization Design
After investigation, in Linux, the host can be shut down (halt), power-off (power-off) and rebooted (reboot) through the shutdown command. You can view the command details through the shutdown command help document. The relevant commands are as follows:
# The system will shut down after 1 minute, if no time is added, the default is to execute after 1 minute
shutdown -H
# The system powers off immediately
shutdown -P now
# The system is forced to restart after 2 minutes
shutdown -r -f +2
# Cancel the shutdown command
shutdown -c
Mapping with the ChaosBlade chaos engineering experimental model, shutdown can be used as the target, halt, poweroff, and reboot can be used as the action respectively, and the forced operation force and time parameter setting are supported. Note that in order to be more suitable for users, the time parameter needs to be modified. If this parameter is not filled in, it means that it will be executed immediately, and the default value will be changed to now. Then use chaosblade to execute as follows:
# The system shuts down after 1 minute, if no time is added, the default is to execute immediately
blade create shutdown halt --time 1
# The system powers off immediately
blade create shutdown poweroff --force
# The system is forced to restart after 2 minutes
blade create shutdown reboot --time 2
#Cancel the shutdown command
blade destroy UID
Scenario Code Implementation
Case Reference
The extended failure scenario is similar to the process failure scenario, such as killing a process and stopping a process, which can be realized by referring to the process scenario.
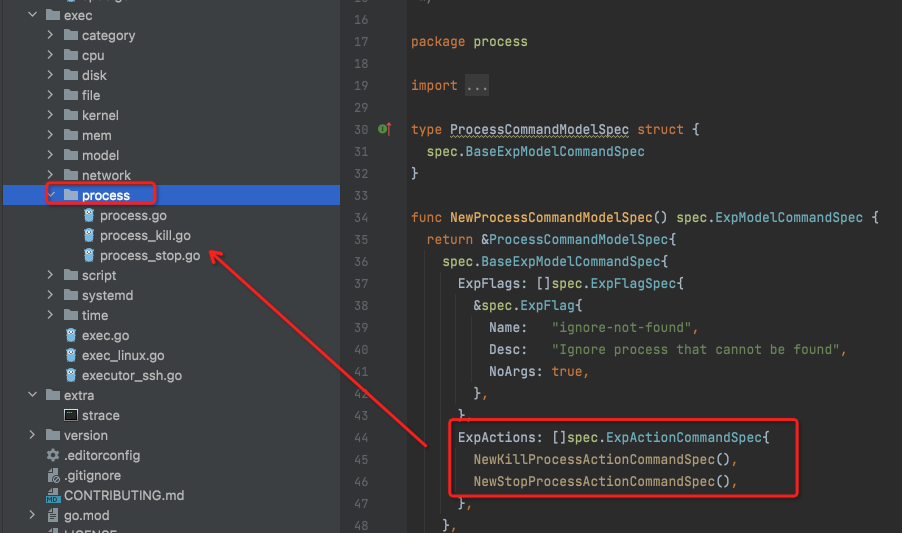
It can be seen from the existing process scene code that in the exec directory, create a process directory to define the target is the process failure scene model definition ProcessCommandModelSpec, in this model respectively define the kill process kill scene and stop process stop scene experimental action model NewXXXProcessActionCommandSpec, Each scenario is defined in process_kill.go and process_stop.go respectively.
Taking KillProcessActionCommandSpec as an example, the following content needs to be defined mainly according to BaseExpActionCommandSpec:
// Fault Scenario Matching Conditions
ActionMatchers []ExpFlagSpec
// Fault related parameters
ActionFlags []ExpFlagSpec
// Failure Scenario Executor
ActionExecutor Executor
// Long description of the failure scenario
ActionLongDesc string
// Failure Scenario Use Cases
ActionExample string
// The executor used by the failure scenario execution
ActionPrograms []string
// Failure scene directory
ActionCategories []string
// Whether the daemon runs persistently in the fault scenario
ActionProcessHang bool
The following will introduce in detail from the creation of the Shutdown fault experiment command, to the realization of the restart experiment scenario, to the realization of the shutdown experiment scenario, to the extraction of the same implementation, and to the expansion of the power outage experiment scenario.
Create a shutdown fault command
Create a shutdown directory in the exec directory to store scene-related codes, and create a shutdown.go file to define the experimental scene model.
package shutdown
import (
"github.com/chaosblade-io/chaosblade-spec-go/spec"
)
type ShutdownCommandModelSpec struct {
spec.BaseExpModelCommandSpec
}
func NewShutdownCommandModelSpec() spec.ExpModelCommandSpec {
return &ShutdownCommandModelSpec{
spec.BaseExpModelCommandSpec{
ExpActions: []spec.ExpActionCommandSpec{
// 重启、关机、断电实现
},
ExpFlags: []spec.ExpFlagSpec{
// 通用参数
},
},
}
}
func (s ShutdownCommandModelSpec) Name() string {
return "shutdown"
}
func (s ShutdownCommandModelSpec) ShortDesc() string {
return "Support shutdown, halt or reboot experiment."
}
func (s ShutdownCommandModelSpec) LongDesc() string {
return "Support shutdown, halt or reboot experiment. Can control shutdown or restart behavior with different flags. Warning! the experiment cannot be recovered by this tool."
}
Next, you need to create reboot, shutdown, and power-off related scenarios in ExpActions, and then take the restart scenario as an example
Implement the reboot scenario
Create shutdown_reboot.go file, follow spec.ExpActionCommandSpec definition RebootActionCommandSpec implementation.
type RebootActionCommandSpec struct {
spec.BaseExpActionCommandSpec
}
func NewRebootActionCommandSpec() spec.ExpActionCommandSpec {
return &RebootActionCommandSpec{
spec.BaseExpActionCommandSpec{
ActionMatchers: []spec.ExpFlagSpec{},
ActionFlags: []spec.ExpFlagSpec{},
ActionExecutor: &RebootExecutor{},
ActionExample: `
# Force to reboot machine
blade c shutdown reboot --force
# Reboot machine after 1 minute
blade c shutdown reboot --time 1`,
ActionPrograms: []string{},
ActionCategories: []string{},
ActionProcessHang: true,
},
}
}
func (r *RebootActionCommandSpec) Name() string {
return "reboot"
}
func (r *RebootActionCommandSpec) Aliases() []string {
return []string{"s"}
}
func (r *RebootActionCommandSpec) ShortDesc() string {
return "Reboot machine"
}
func (r *RebootActionCommandSpec) LongDesc() string {
return "Reboot machine. Warning! the experiment cannot be recovered by this tool."
}
type RebootExecutor struct {
channel spec.Channel
}
func (r *RebootExecutor) Name() string {
return "reboot"
}
func (r *RebootExecutor) Exec(uid string, ctx context.Context, model *spec.ExpModel) *spec.Response {
// TODO 重启具体实现
return nil
}
func (r *RebootExecutor) SetChannel(channel spec.Channel) {
r.channel = channel
}
According to the above scenario design section, use the system shutdown command to implement the machine reboot operation, and support time and enforcement parameters. It is coded and implemented in the Exec function.
func (r *RebootExecutor) Exec(uid string, ctx context.Context, model *spec.ExpModel) *spec.Response {
// Use it to identify operation
if _, ok := spec.IsDestroy(ctx); ok {
return cancel(ctx, uid, model, r.channel)
}
return execute(ctx, model, "-r", r.channel)
}
// Execute shutdown command
func execute(ctx context.Context, model *spec.ExpModel, command string, channel spec.Channel) *spec.Response {
response := checkShutdownCommand(channel)
if !response.Success {
return response
}
force := model.ActionFlags[Force.Name] == "true"
time := model.ActionFlags[Time.Name]
if time == "" {
time = "now"
}
command = fmt.Sprintf("%s %s", ShutdownCommand, command)
if force {
command = fmt.Sprintf("%s -f", command)
}
command = fmt.Sprintf("sleep %d && %s %s", SleepTime, command, time)
shutdownErrLog := util.GetNohupOutput(util.Bin, stderrLog)
// nohup bash -c "sleep 3 && shutdown -k" < /dev/null >/dev/null 2> shutdown.err &
command = fmt.Sprintf("bash -c '%s' < /dev/null > /dev/null 2> %s", command, shutdownErrLog)
return channel.Run(ctx, "nohup", command)
}
// Cancel shutdown
func cancel(ctx context.Context, uid string, model *spec.ExpModel, channel spec.Channel) *spec.Response {
time := model.ActionFlags[Time.Name]
if time == "" || time == "now" || time == "+0" {
return spec.ReturnSuccess(uid)
}
// Calling the cancel command directly will not process the execution result.
// Because the return may fail due to downtime, it returns success directly.
response := channel.Run(ctx, ShutdownCommand, "-c")
if !response.Success {
logrus.Warningf("uid: %s, shutdown cancel failed, %v", uid, response.Error())
}
// Not bug.
return spec.ReturnSuccess(uid)
}
After the restart scenario is implemented, this scenario can be added to the shutdown command:
func NewShutdownCommandModelSpec() spec.ExpModelCommandSpec {
return &ShutdownCommandModelSpec{
spec.BaseExpModelCommandSpec{
ExpActions: []spec.ExpActionCommandSpec{
NewRebootActionCommandSpec(),
},
ExpFlags: []spec.ExpFlagSpec{
&Time, &Force,
},
},
}
}
The shutdown_halt.go and shutdown_poweroff.go implementations can also be added in this way. Since the shutdown command controls shutdown, power-off, and reboot operations through parameters, the general code can be extracted into the shutdown.go file, and other scene files can call the functions in this file. The final code is as follows:

shutdown_halt.go codes:
func (h *HaltExecutor) Exec(uid string, ctx context.Context, model *spec.ExpModel) *spec.Response {
if _, ok := spec.IsDestroy(ctx); ok {
return cancel(ctx, uid, model, h.channel)
}
return execute(ctx, model, "-H", h.channel)
}
shutdown_poweroff.go codes:
func (p *PowerOffExecutor) Exec(uid string, ctx context.Context, model *spec.ExpModel) *spec.Response {
if _, ok := spec.IsDestroy(ctx); ok {
return cancel(ctx, uid, model, p.channel)
}
return execute(ctx, model, "-P", p.channel)
}
shutdown_reboot.go codes:
func (r *RebootExecutor) Exec(uid string, ctx context.Context, model *spec.ExpModel) *spec.Response {
if _, ok := spec.IsDestroy(ctx); ok {
return cancel(ctx, uid, model, r.channel)
}
return execute(ctx, model, "-r", r.channel)
}
So far, the shutdown, power-off, and restart experiment scenarios involved in shutdown have been realized, just register to the model_linux.go experiment list:
func GetAllExpModels() []spec.ExpModelCommandSpec {
return []spec.ExpModelCommandSpec{
cpu.NewCpuCommandModelSpec(),
mem.NewMemCommandModelSpec(),
process.NewProcessCommandModelSpec(),
network.NewNetworkCommandSpec(),
disk.NewDiskCommandSpec(),
script.NewScriptCommandModelSpec(),
file.NewFileCommandSpec(),
kernel.NewKernelInjectCommandSpec(),
systemd.NewSystemdCommandModelSpec(),
stressng.NewStressModelSpec(),
time.NewTimeCommandSpec(),
// shutdown
shutdown.NewShutdownCommandModelSpec(),
}
}
Package Test
Use make build in the project root directory to compile. After compilation, chaos_os will be generated in target/chaosblade-VERSION/bin and chaosblade-os-spec-XXX.yaml files will be generated in target/chaosblade-VERSION/yaml. In this file There will be a shutdown scenario statement:
- target: shutdown
shortDesc: Support shutdown, halt or reboot experiment.
longDesc: Support shutdown, halt or reboot experiment. Can control shutdown or restart
behavior with different flags. Warning! the experiment cannot be recovered by
this tool.
actions:
- action: halt
aliases: [h]
shortDesc: Halt machine
longDesc: Halt machine. Warning! the experiment cannot be recovered by this tool.
flags:
- name: time
desc: waiting time, unit is minute, for example +1 means after 1 minute to run
noArgs: false
required: false
requiredWhenDestroyed: false
- name: force
desc: Force operation
noArgs: true
required: false
requiredWhenDestroyed: false
测试
Directly replace the above compiled file with the corresponding file in the original chaosblade toolkit and test it.
./blade c shutdown -h
Support shutdown, halt or reboot experiment. Can control shutdown or restart behavior with different flags. Warning! the experiment cannot be recovered by this tool.
Usage:
blade create shutdown [flags]
blade create shutdown [command]
Available Commands:
halt Halt machine
poweroff Shutdown machine
reboot Reboot machine
Flags:
-h, --help help for shutdown
Global Flags:
-a, --async whether to create asynchronously, default is false
-d, --debug Set client to DEBUG mode
-e, --endpoint string the create result reporting address. It takes effect only when the async value is true and the value is not empty
-n, --nohup used to internal async create, no need to config
--uid string Set Uid for the experiment, adapt to docker and cri
Use "blade create shutdown [command] --help" for more information about a command.